Apolipoprotein E fragment (133-149) – COG133: acetyl-LRVRLASHLRKLRKRLL-NH2 (CAS : 514200-66-9)
SB-PEPTIDE offers Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) mimetic peptide COG133 – LRVRLASHLRKLRKRLL – which competes with the ApoE holoprotein for binding the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor.
Apolipoprotein E (ApoE): A key player in lipid transport and beyond
Apolipoprotein E (apoE) is a low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor ligand that belongs to the family of fat-binding proteins,known as apolipoproteins. While the liver and macrophages primarily produce ApoE in peripheral tissues to mediate cholesterol metabolism,in the central nervous system (CNS),astrocytes take the lead in producing ApoE.
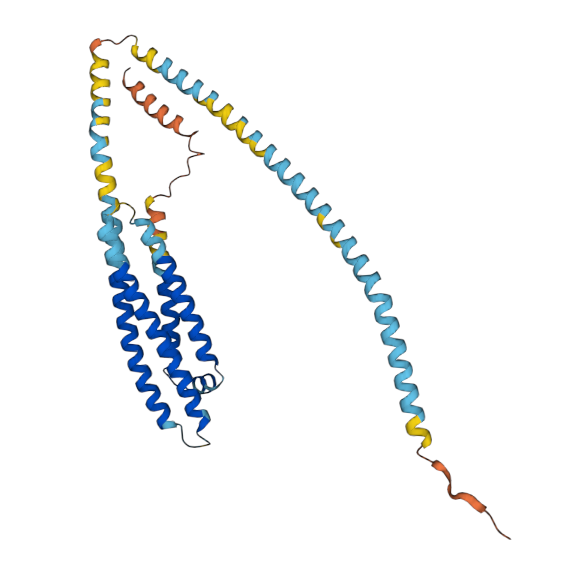
ApoE plays a vital role in lipid transport,facilitating the movement of lipids such as fats,cholesterol,and fat-soluble vitamins between organs via plasma and interstitial fluids. In the central CNS,it serves as a crucial cholesterol carrier,promoting neuron survival,sprouting,and exhibiting functional anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects.
Beyond its role in lipid transport,ApoE binds to a diverse range of cellular receptors,influencing immune responses,promoting cell migration,and potentially impacting transcription regulation.
With its multifaceted functions,ApoE stands as a cornerstone in maintaining plasma and tissue lipid homeostasis and orchestrating complex interplays within the body.
ApoE(133-149) mimetic peptide : COG 133
COG 133 mimetic peptide,takes the incredible capabilities of acting the same way as the LDL receptor-binding domain of ApoE. Therefore,this peptide wields a non-competitive stance against the alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor,which is not only implicated in long-term memory but also in neurotoxicity,stroke,myocardial infarction,sepsis,Alzheimer’s disease,cancer progression,and angiogenic/neurogenic activity. Moreover,COG133’s anti-apoptotic effects further accentuate its potential.
By mimicking ApoE,COG 133 / ApoE(133-149) masterfully inhibits the NMDA receptor channel function through interactions with the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. The peptide emerged as a potent agent in reducing inflammation,cellular infiltration,and demyelination,making strides in animal models of multiple sclerosis (MS) and the 5-fluorouracil model of intestinal mucositis.
Indeed,COG-133 emerged as a champion to suppress symptoms of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE),curbing inflammation,demyelination,and cell infiltration in the spinal cord. ApoE (133-149) fragment additionally showcased its prowess by decreasing TNF-α and nitric oxide (NO) release in BV-2 microglia and counteracting LPS-induced increases in brain levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in mice. The peptide also stands as a guardian of hippocampal neuronal health and offers promise in delaying disease onset and reducing severity of EAE mouse model.
COG-133 applications
The applications of COG 133 (ApoE 133-149) resonate across diverse fields of research and healthcare.
Generally speaking,COG133’s multifaceted influences on inflammation,cellular responses,and neuronal health open doors to novel therapies for neurological disorders.
Its potential as a groundbreaking tool in understanding and combating MS holds the promise of improved treatments and enhanced quality of life for patients suffering from this particular disease.
SB-PEPTIDE is proud to offer this remarkable peptide for neurological research!
Technical specification
 |
Sequence : acetyl-LRVRLASHLRKLRKRLL-NH2 |
 |
MW : 2169 ,72 g/mol (C97H181N37O19) |
 |
Purity : > 95% |
 |
Counter-Ion : TFA Salts (see option TFA removal) |
 |
Delivery format : Freeze dried in propylene 2mL microtubes |
 |
Other names : ApoE (133-149) |
 |
Peptide Solubility Guideline |
 |
Bulk peptide quantities available |
Price
| Product catalog | Size | Price € HT | Price $ USD |
| SB180-1MG | 1 mg | 121 | 151 |
| SB180-5MG | 5 mg | 424 | 529 |
| SB180-25MG | 25 mg | 1100 | 1375 |
References
Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021 Jan 08;8:621144. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.621144
ApoPred: Identification of Apolipoproteins and Their Subfamilies With Multifarious Features
Apolipoprotein is a group of plasma proteins that are associated with a variety of diseases,such as hyperlipidemia,atherosclerosis,Alzheimer’s disease,and diabetes. In order to investigate the function of apolipoproteins and to develop effective targets for related diseases,it is necessary to accurately identify and classify apolipoproteins. Although it is possible to identify apolipoproteins accurately through biochemical experiments,they are expensive and time-consuming. This work aims to establish a high-efficiency and high-accuracy prediction model for recognition of apolipoproteins and their subfamilies. We firstly constructed a high-quality benchmark dataset including 270 apolipoproteins and 535 non-apolipoproteins. Based on the dataset,pseudo-amino acid composition (PseAAC) and composition of k-spaced amino acid pairs (CKSAAP) were used as input vectors. To improve the prediction accuracy and eliminate redundant information,analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to rank the features. And the incremental feature selection was utilized to obtain the best feature subset. Support vector machine (SVM) was proposed to construct the classification model,which could produce the accuracy of 97.27%,sensitivity of 96.30%,and specificity of 97.76% for discriminating apolipoprotein from non-apolipoprotein in 10-fold cross-validation. In addition,the same process was repeated to generate a new model for predicting apolipoprotein subfamilies. The new model could achieve an overall accuracy of 95.93% in 10-fold cross-validation. According to our proposed model,a convenient webserver called ApoPred was established,which can be freely accessed at http://tang-biolab.com/server/ApoPred/service.html. We expect that this work will contribute to apolipoprotein function research and drug development in relevant diseases.
